TOPLINE:
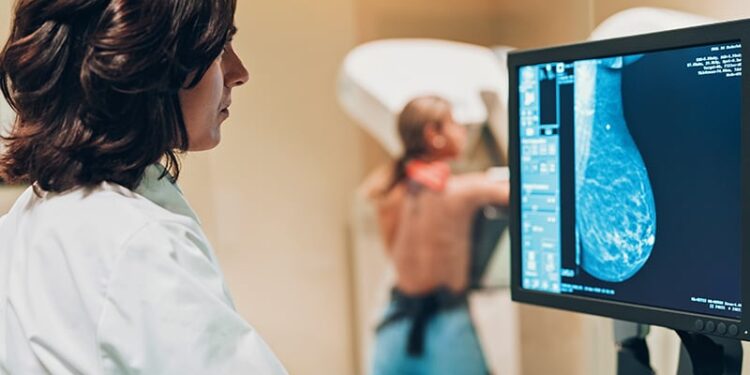
An artificial intelligence (AI) tool in mammography showed a high sensitivity and specificity, outperforming human readers in overall performance, a study found. However, the performance of the AI tool was slightly lower at the lesion level than at the breast level.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively analysed mammograms from the UK’s NHS Breast Screening Programme by using a commercial AI tool (Lunit Insight MMG) and human readers to evaluate 882 non-malignant and 318 malignant breasts with 328 lesions.
- Human readers (n = 1258), including radiologists, radiographers, and breast clinicians, reviewed 1200 mammograms. The same cases were independently reviewed by the AI tool.
- Human and AI decisions to clear or recall breasts or lesions were compared with real outcomes on the basis of pathology or a 3-year follow-up.
- Sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated at both breast and lesion (marked regions of interest) levels.
TAKEAWAY:
- The AI tool outperformed human readers on the basis of the AUC at the breast level (0.942 vs 0.878) and lesion level (0.929 vs 0.851; P < .01 for both).
- At the developer-recommended recall threshold, the AI tool achieved a significantly higher specificity than human readers at the breast level (87.4% vs 79.2%; P < .01).
- When calibrated to match the human specificity, the AI tool had a higher sensitivity than human readers at the breast level (92.1% vs 87.5%; P = .051) and lesion level (90.9% vs 83.2%; P < .01).
- The AI tool failed to localise 4% of total cancer lesions, with a median human error rate of 62.6%.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings support the notion of implementing AI into a prospective screening workflow, where the localisation of malignancies is beneficial to patients and the screening process,” the authors wrote. “To improve human-AI collaboration, AI should be assessed at the lesion level; poor accuracy here may lead to automation bias and unnecessary patient procedures,” they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Adnan Gani Taib and George John William Partridge, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, England. It was published online on June 25, 2025, in European Radiology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study could not assess the real-time effect of AI on human decision-making due to its retrospective design. The use of cancer-enriched test sets may have led to an overestimation of human performance. Additionally, prior mammograms were not available for comparison, which are often used in routine clinical practice to aid detection.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Lunit. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Source link : https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/artificial-intelligence-outperforms-humans-mammography-2025a1000i6g?src=rss
Author :
Publish date : 2025-07-11 12:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.