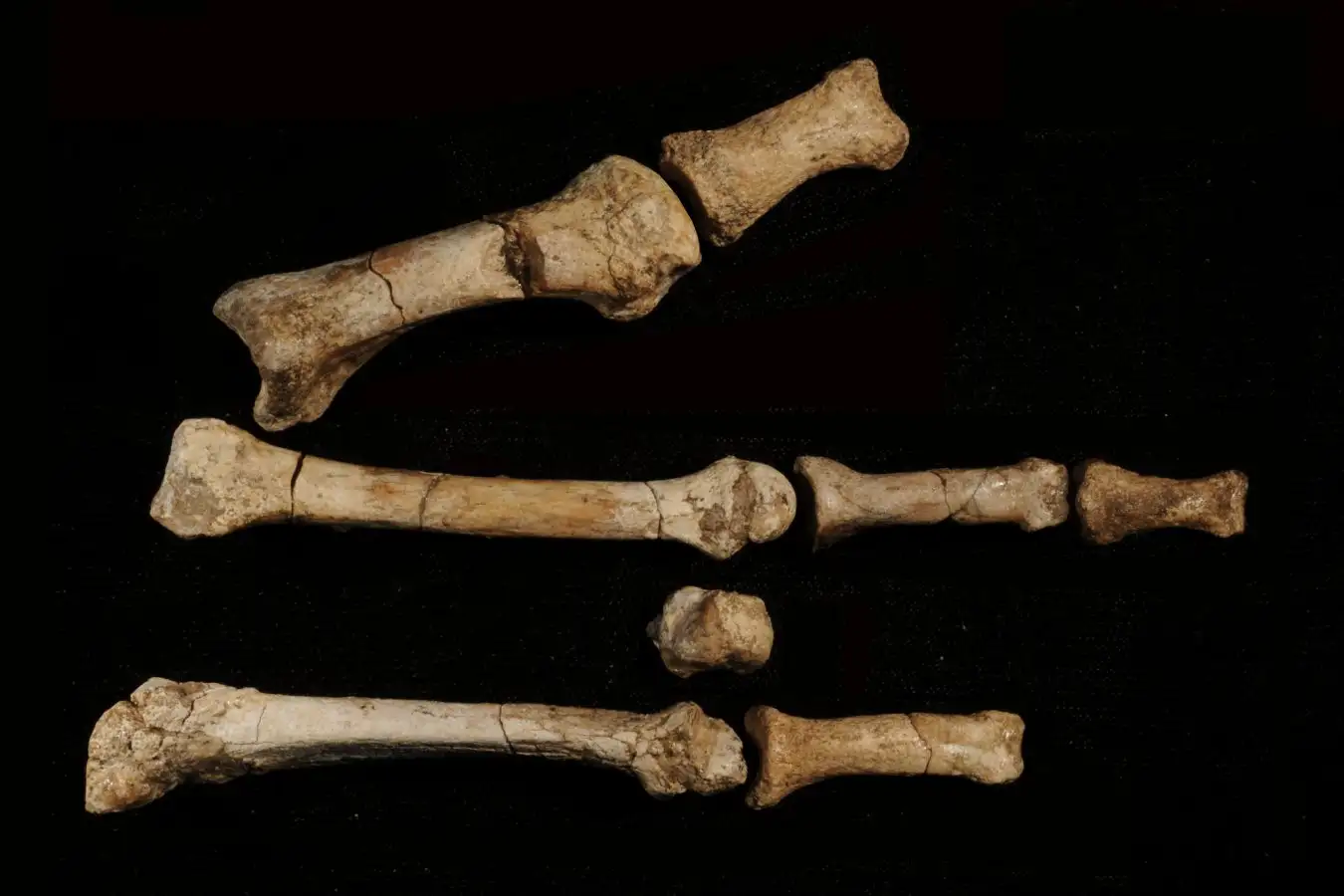
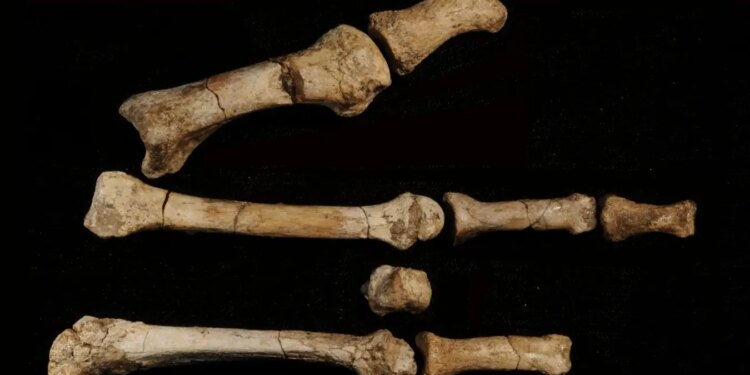
The ancient human foot bones have been a mystery since they were discovered by scientists in 2009
Yohannes Haile-Selassie
The provenance of 3.4-million-year-old foot bones in Ethiopia may have finally been solved – and could prompt a rethink into how our various ancient human ancestors coexisted.
In 2009, Yohannes Haile-Selassie at Arizona State University and his colleagues found eight hominin bones, that once made up a right foot, at a site known as Burtele in the Afar region of north-eastern Ethiopia.
The find, christened the Burtele foot, included a gorilla-like opposable big toe, suggesting that whichever species it belonged to was able to climb trees.
Although another ancient hominin species, Australopithecus afarensis, was known to live nearby – most famously represented by the fossil Lucy, also found in the Afar region – the Burtele foot seemed to be from a different one. “We knew from the very beginning that it didn’t belong to Lucy’s species,” says Haile-Selassie.
The two main possibilities that gnawed at Haile-Selassie were whether the foot belonged to another species within the genus Australopithecus or a much older, more primitive one called Ardipithecus, which inhabited Ethiopia more than a million years earlier, but also had an opposable big toe.
In the meantime, the recovery of jaw and teeth remains from the same locality led the researchers to announce the discovery of a new-to-science hominin species in 2015, which they named Australopithecus deyiremeda. They suspected that the mysterious foot bones belonged to A. deyiremeda, but these were a different age to the jaw and teeth remains, so the team couldn’t be sure.
But the next year, the researchers found an A. deyiremeda’s lower jawbone within 300 metres of where the foot was recovered, with both remains being the same geological age. Based on this, the team has concluded that the foot bones belonged to A. deyiremeda.
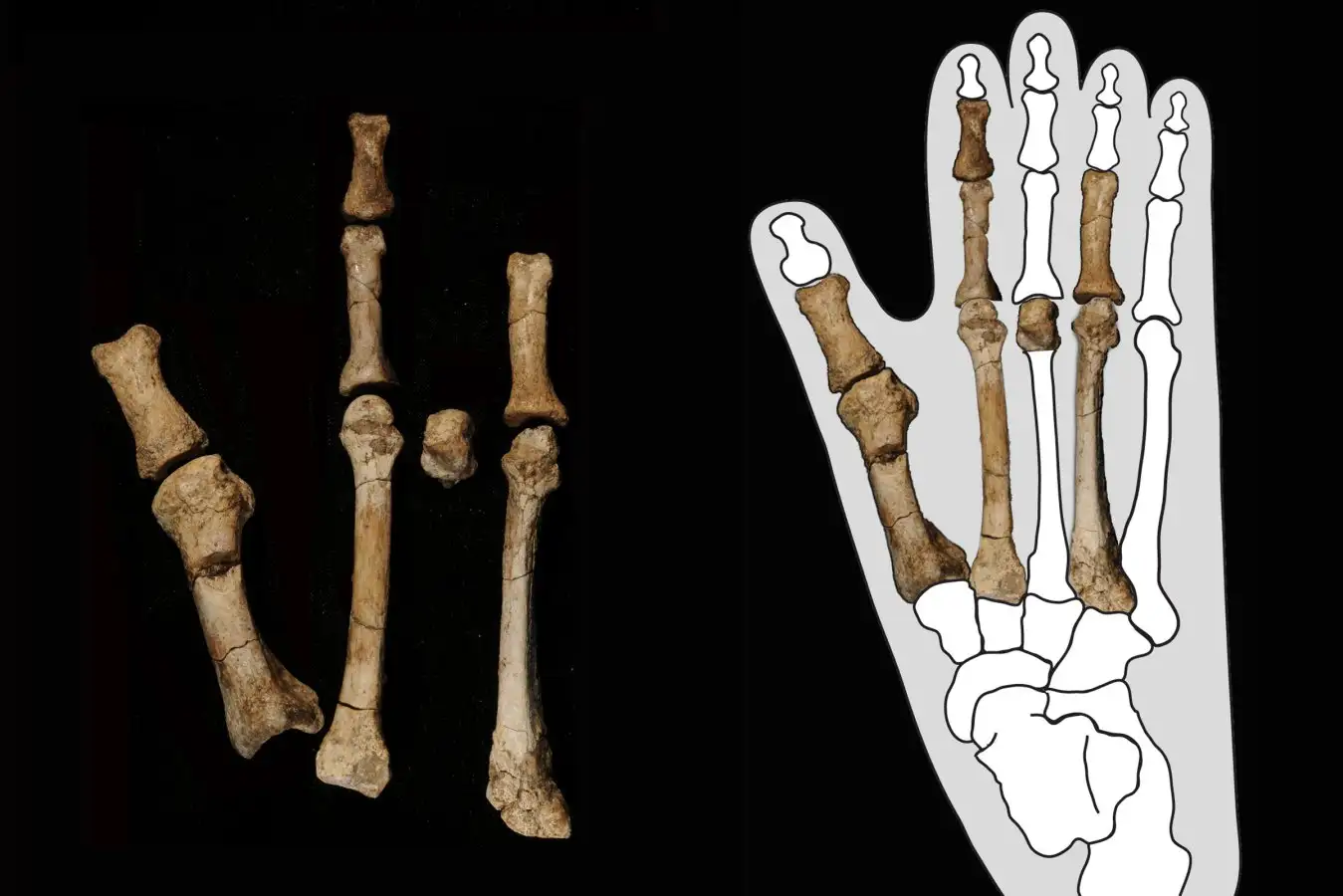
The Burtele foot (left) and the bones embedded in an outline of a gorilla foot (right), which was similar to that of Australopithecus deyiremeda
Yohannes Haile-Selassie
In another part of the experiment, where the researchers studied the carbon isotopes of the A. deyiremeda teeth, they determined that the species mostly consumed material from trees and shrubs, whereas teeth of A. afarensis indicate a diet much richer in grasses.
The discoveries prove that two species of hominin lived together in the same environment, says Haile-Selassie. The groups weren’t competing for food, so it is possible they coexisted peacefully, he says.
“They must have seen each other, spent time in the same area doing their own things,” he says. “One may have seen members of Australopithecus deyiremeda in the trees while members of A. afarensis were roaming in the grasslands nearby.”
The findings also expand our knowledge of human evolution. “Some had argued that there was only one hominin species at any given time giving rise to a newer form,” says Haile-Selassie. “Now, we know that our evolution was not linear. There were multiple closely related hominin species living at the same time even in close geographic proximity and living in harmony, suggesting that coexistence is deep in our ancestry.”
Carrie Mongle at Stony Brook University in New York says it is “exciting we are starting to get a better understanding of hominin diversity in the Pliocene [around 3 million years ago]”.
Topics:
- human evolution/
- ancient humans
Source link : https://www.newscientist.com/article/2505923-ancient-human-foot-bones-shed-light-on-how-two-species-coexisted/?utm_campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utm_source=NSNS&utm_medium=RSS&utm_content=home
Author :
Publish date : 2025-11-26 16:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.