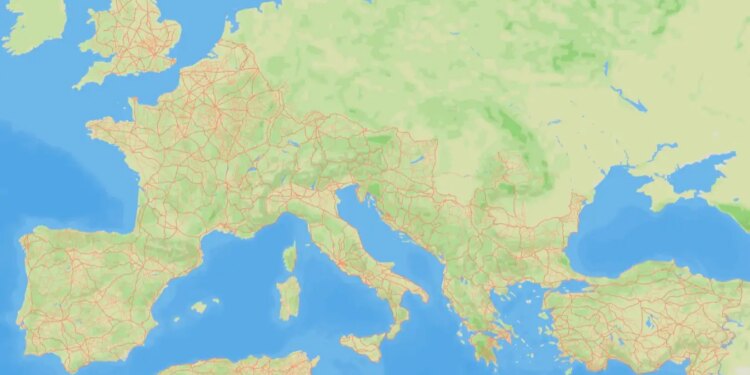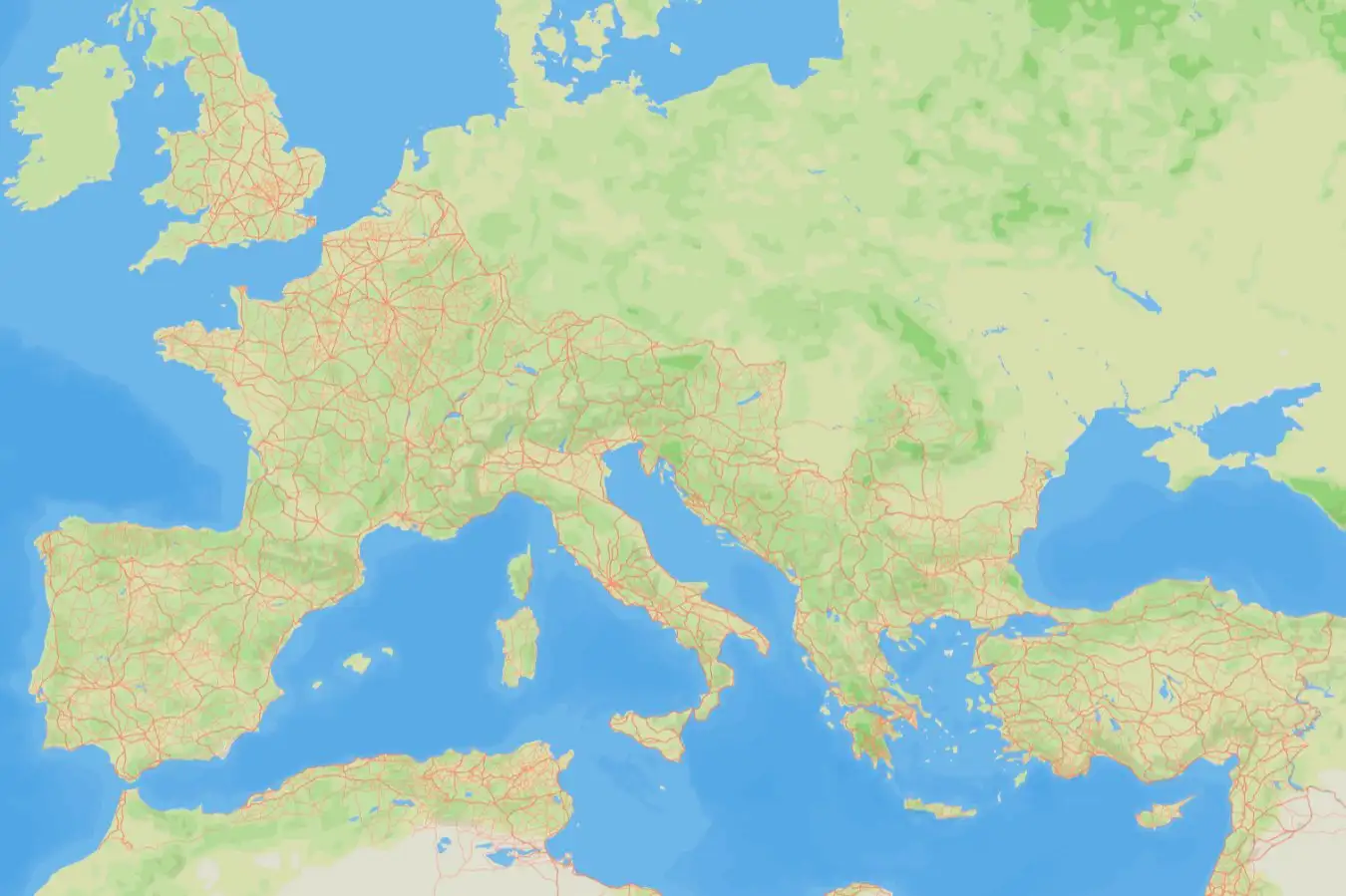
The Roman road network mapped by Itiner-e
Itiner-e
A comprehensive new map of Roman roads has boosted the known size of the empire’s land transport network by almost 60 per cent – and it is available for anyone to explore online.
The project, called Itiner-e, brings together topographic mapping, satellite imagery and centuries of historical records in what its creators say is the first open dataset of its kind.
“It emerged from enormous frustration,” says Tom Brughmans at Aarhus University in Denmark. “It’s like the most enigmatic topic in Roman archaeology. We even have proverbs that say, ‘All roads lead to Rome’. So why on Earth can’t I download all the Roman roads? Where are they?”
Brughmans and his colleagues incorporated evidence from a large set of studies and traced more realistic paths for previously known routes to produce a map of the road network as it might have looked around AD 150. They also gave the placement of each stretch of road a confidence rating, based on the quality of the source.
According to their data, the total length of the road network at this time was around 299,171 kilometres – much more than the previous estimate of 188,555 kilometres given by the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World.
The dataset also reveals that, although we have strong evidence for the starts and ends of many roads, only 2.8 per cent of the network’s length can be located precisely – within 50 metres in mountains and 200 metres on flat land.
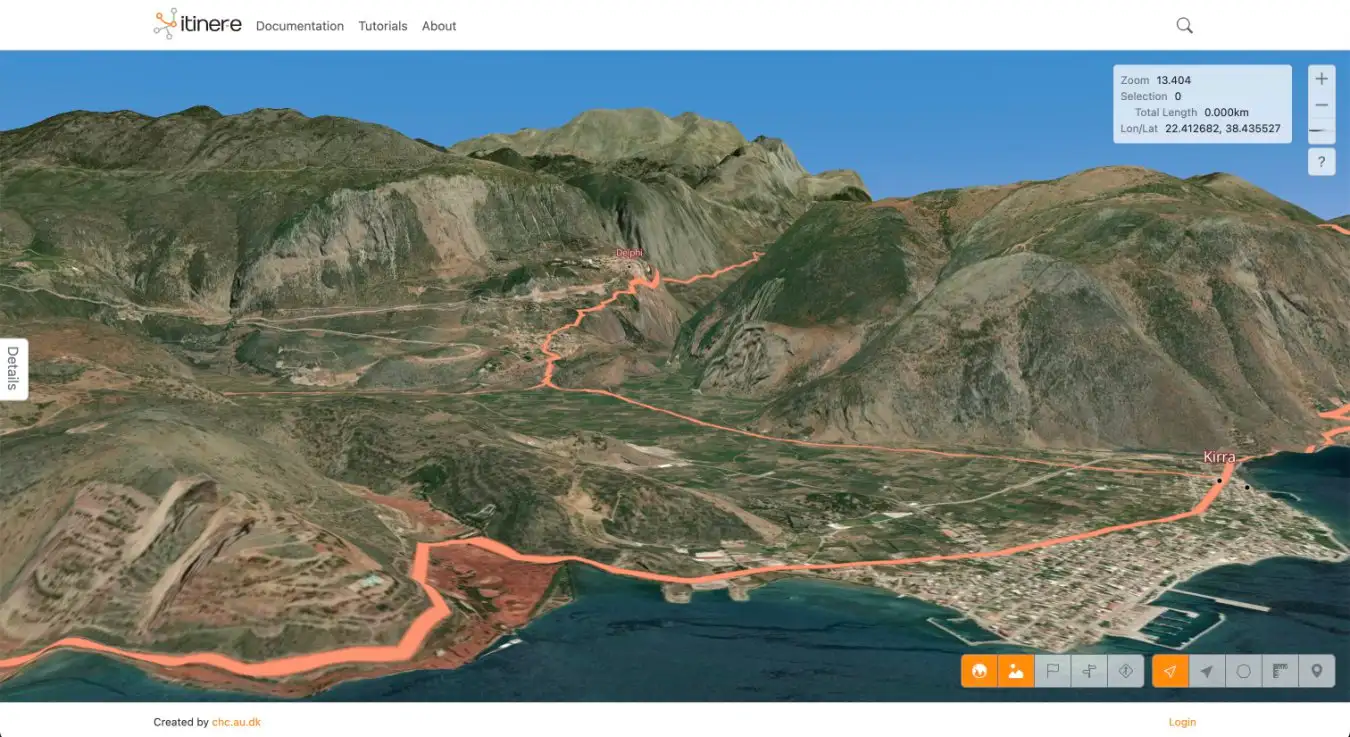
The Roman roads through mountain passes leading to Delphi in ancient Greece
Itiner-e
For Brughmans, this reflects how difficult it can be to get funding to excavate entire Roman roads, which means a lot of work simply hasn’t been done. Major roads have also been built over many times throughout history, so it can be difficult to uncover the original path.
Although Roman roads are famous for being straight, it is a myth that they always were, says Catherine Fletcher at Manchester Metropolitan University in the UK, who wasn’t involved in the study. “Straight wasn’t always cheap or practical, especially through mountainous terrain,” she says. “Often, where there was a pre-existing route in place, the Romans would adapt it rather than build anew.”
Improved knowledge of the Roman road network can potentially inform our understanding of many highly impactful events in European history. The emergence of early Christianity, mass migration and continent-wide pandemics are all phenomena that were influenced by the Roman road system, says Brughmans.
Despite their importance, roads often get overlooked because they aren’t as glamorous as amphitheatres and gladiators, says Fletcher. “[It’s like that] famous scene in Monty Python,” she says, “where they’re talking about what the Romans did for us, and they go, ‘And the roads… Well, obviously the roads! The roads go without saying’.”

Historic Herculaneum – Uncovering Vesuvius, Pompeii and ancient Naples
Embark on a captivating journey where history and archaeology come to life through Mount Vesuvius and the ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
Topics:
Source link : https://www.newscientist.com/article/2503325-digital-map-lets-you-explore-the-roman-empires-vast-road-network/?utm_campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utm_source=NSNS&utm_medium=RSS&utm_content=home
Author :
Publish date : 2025-11-06 16:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.