TOPLINE:
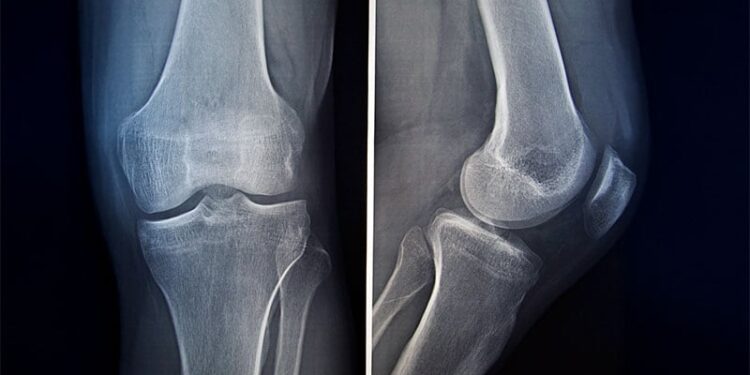
In patients with osteogenesis imperfecta, artificial intelligence (AI) assistance improved the fracture detection accuracy of radiologists from 83.4% to 90.7%. However, radiologists performed better than AI when their standalone performance was considered.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this study, researchers analysed 336 appendicular and pelvic radiographs of 48 children (mean age, 12 years) with genetically confirmed osteogenesis imperfecta.
- The ground truth was determined by a consensus opinion of two consultant paediatric radiologists who labelled acute and healing fractures with bounding boxes.
- Seven radiologists independently evaluated anonymised images in two rounds — the first round without AI and the second round with AI assistance. The AI tool provided bounding boxes for suspected fractures but did not distinguish acute from healing fractures.
- After both rounds were completed, the results from radiologists without AI assistance, radiologists with AI assistance, and the AI alone were compared against the ground truth by calculating the intersection between the bounding boxes.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI demonstrated a per-examination accuracy of 74.8% (95% CI, 65.4%-82.7%), compared with the average radiologist performance of 83.4% (95% CI, 75.2%-89.8%).
- Radiologists using AI assistance improved their average accuracy per examination to 90.7% (95% CI, 83.5%-95.4%).
- AI support increased average radiologist per-image accuracy by 7.0% (from 84.6% to 91.6%) and per-fracture accuracy by 3.7% (from 76.3% to 80.0%).
- Per fracture, AI assistance lowered true and false positives while raising true and false negatives, boosting the accuracy by 3.7%, specificity by 10.0%, and positive predictive value by 7.2%.
- On average, radiologists changed their per-fracture decisions in 72 instances; 69% of those changes matched the AI’s suggestion, and 64% improved accuracy.
IN PRACTICE:
“In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that AI assistance improves radiologists’ performance in diagnosing fractures in children with OI [osteogenesis imperfecta], even if it is not specifically trained for this population,” the authors of the study wrote. “Nevertheless, compared to radiologists, the standalone AI performance was worse, thus highlighting potential dangers of implementing the AI tool in an autonomous manner,” they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Cato Pauling, University College London, London, England. It was published online on July 07, 2025, in European Radiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers included repeat examinations from some patients over the study period, which may have introduced bias due to similarities in appearances. This study used only one commercially available AI model, despite multiple products being available in the market. Additionally, the lack of a control group of patients without bone fragility disorder made it challenging to objectively evaluate whether the AI tool performed less accurately in children with osteogenesis imperfecta.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding support from the National Institute for Health and Care Research. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Source link : https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/can-artificial-intelligence-aid-fracture-detection-children-2025a1000irl?src=rss
Author :
Publish date : 2025-07-18 12:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.