A dangerous strain of bird flu is spreading in US livestock
MediaMedium/Alamy
Since Donald Trump assumed office in January, the leading US public health agency has pulled back preparations for a potential bird flu pandemic. But as it steps back, another government agency is stepping up.
While the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) previously held regular briefings on its efforts to prevent a wider outbreak of a deadly bird flu virus called H5N1 in people, it largely stopped once Trump took office. It has also cancelled funding for a vaccine that would have targeted the virus. In contrast, the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) has escalated its fight against H5N1’s spread in poultry flocks and dairy herds, including by funding the development of livestock vaccines.
This particular virus – a strain of avian influenza called H5N1 – poses a significant threat to humans, having killed about half of the roughly 1000 people worldwide who tested positive for it since 2003. While the pathogen spreads rapidly in birds, it is poorly adapted to infecting humans and isn’t known to transmit between people. But that could change if it acquires mutations that allow it to spread more easily among mammals – a risk that increases with each mammalian infection.
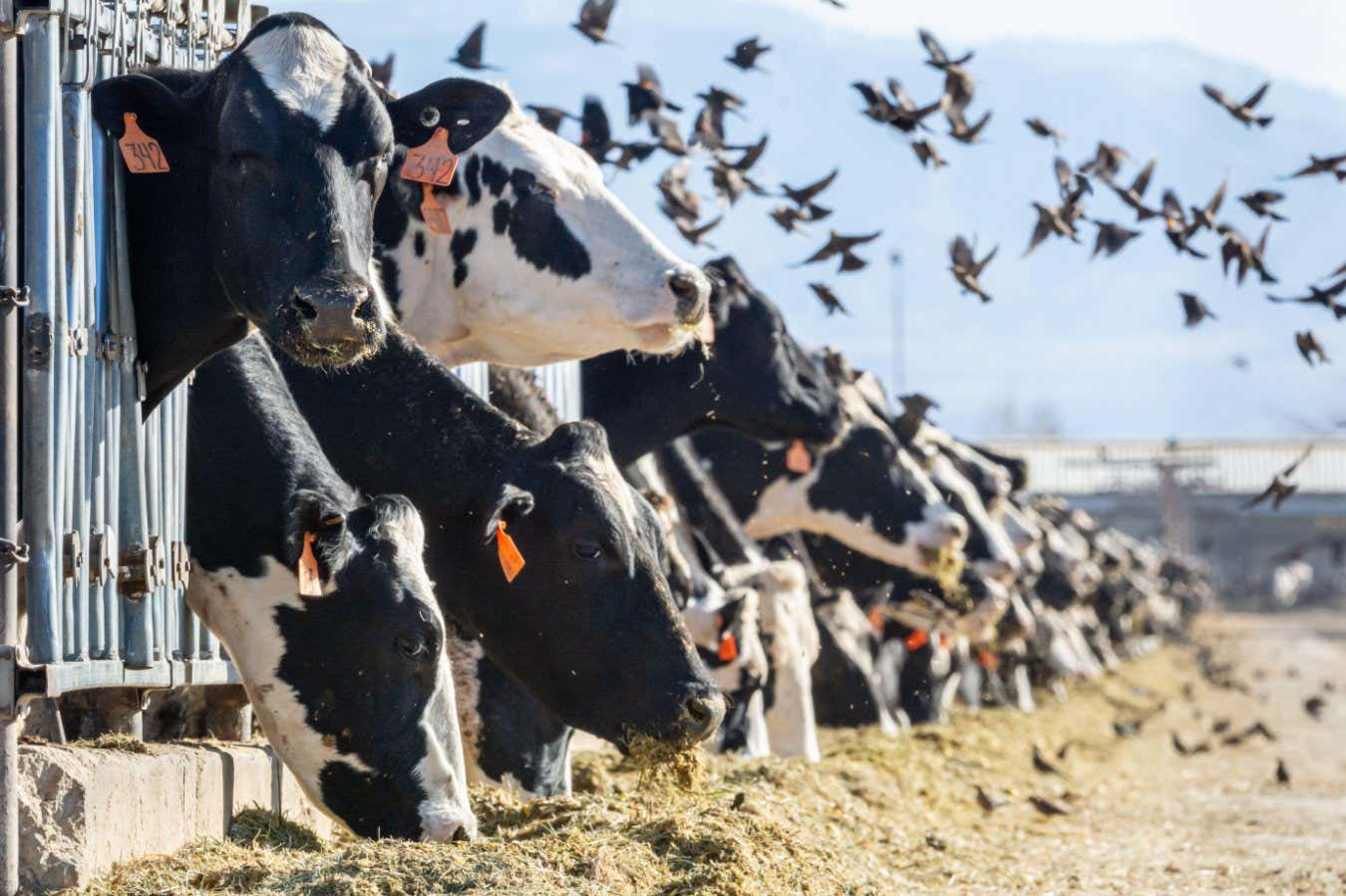
The possibility of H5N1 evolving to become more dangerous to people has grown significantly since March 2024, when the virus jumped from migratory birds to dairy cows in Texas. More than 1,070 herds across 17 states have been affected since then.
H5N1 also infects poultry, placing the virus in closer proximity to people. Since 2022, nearly 175 million domestic birds have been culled in the US due to H5N1, and almost all of the 71 people who have tested positive for it had direct contact with livestock.
“We need to take this seriously because when [H5N1] constantly is spreading, it’s constantly spilling over into humans,” says Seema Lakdawala at Emory University in Georgia. The virus has already killed a person in the US and a child in Mexico this year.
Still, cases have declined under Trump. The last recorded human case was in February, and the number of affected poultry flocks fell 95 per cent between then and June. Outbreaks in dairy herds have also stabilised.
It isn’t clear what is behind the decline. Lakdawala believes it is partly due to a lull in bird migration, which reduces opportunities for the virus to spread from wild birds to livestock. It may also reflect efforts by the USDA to contain outbreaks on farms. In February, the USDA unveiled a $1 billion plan for tackling H5N1, including strengthening farmers’ defences against the virus, such as through free biosecurity assessments. Of the 150 facilities that have undergone assessment, only one has experienced an H5N1 outbreak.
Under Trump, the USDA also continued its National Milk Testing Strategy, which mandates farms provide raw milk samples for influenza testing. If a farm is positive for H5N1, it must allow the USDA to monitor livestock and implement measures to contain the virus. The USDA launched the programme in December and has since ramped up participation to 45 states.
“The National Milk Testing Strategy is a fantastic system,” says Erin Sorrell at Johns Hopkins University in Maryland. Along with the USDA’s efforts to improve biosecurity measures on farms, milk testing is crucial for containing the outbreak, says Sorrell.
But while the USDA has bolstered its efforts against H5N1, the HHS doesn’t appear to have followed suit. In fact, the recent drop in human cases may reflect decreased surveillance due to workforce cuts, says Sorrell. In April, the HHS laid off about 10,000 employees, including 90 per cent of staff at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, an office that helps investigate H5N1 outbreaks in farm workers.
“There is an old saying that if you don’t test for something, you can’t find it,” says Sorrell. Yet a spokesperson for the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says its guidance and surveillance efforts have not changed. “State and local health departments continue to monitor for illness in persons exposed to sick animals,” they told New Scientist. “CDC remains committed to rapidly communicating information as needed about H5N1.”
The USDA and HHS also diverge on vaccination. While the USDA has allocated $100 million toward developing vaccines and other solutions for preventing H5N1’s spread in livestock, the HHS cancelled $776 million in contracts for influenza vaccine development. The contracts – terminated on 28 May – were with the pharmaceutical company Moderna to develop vaccines targeting flu subtypes, including H5N1, that could cause future pandemics. The news came the same day Moderna reported nearly 98 per cent of the roughly 300 participants who received two doses of the H5 vaccine in a clinical trial had antibody levels believed to be protective against the virus.
The US has about five million H5N1 vaccine doses stockpiled, but these are made using eggs and cultured cells, which take longer to produce than mRNA-based vaccines like Moderna’s. The Moderna vaccine would have modernised the stockpile and enabled the government to rapidly produce vaccines in the event of a pandemic, says Sorrell. “It seems like a very effective platform and would have positioned the US and others to be on good footing if and when we needed a vaccine for our general public,” she says.
The HHS cancelled the contracts due to concerns about mRNA vaccines, which Robert F Kennedy Jr – the country’s highest-ranking public health official – has previously cast doubt on. “The reality is that mRNA technology remains under-tested, and we are not going to spend taxpayer dollars repeating the mistakes of the last administration,” said HHS communications director Andrew Nixon in a statement to New Scientist.
However, mRNA technology isn’t new. It has been in development for more than half a century and numerous clinical trials have shown mRNA vaccines are safe. While they do carry the risk of side effects – the majority of which are mild – this is true of almost every medical treatment. In a press release, Moderna said it would explore alternative funding paths for the programme.
“My stance is that we should not be looking to take anything off the table, and that includes any type of vaccine regimen,” says Lakdawala.
“Vaccines are the most effective way to counter an infectious disease,” says Sorrell. “And so having that in your arsenal and ready to go just give you more options.”
Topics:
Source link : https://www.newscientist.com/article/2484143-how-a-us-agriculture-agency-became-key-in-the-fight-against-bird-flu/?utm_campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utm_source=NSNS&utm_medium=RSS&utm_content=home
Author :
Publish date : 2025-06-13 21:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.