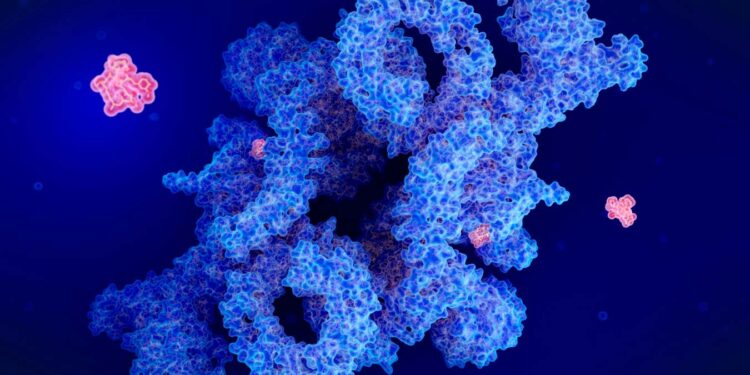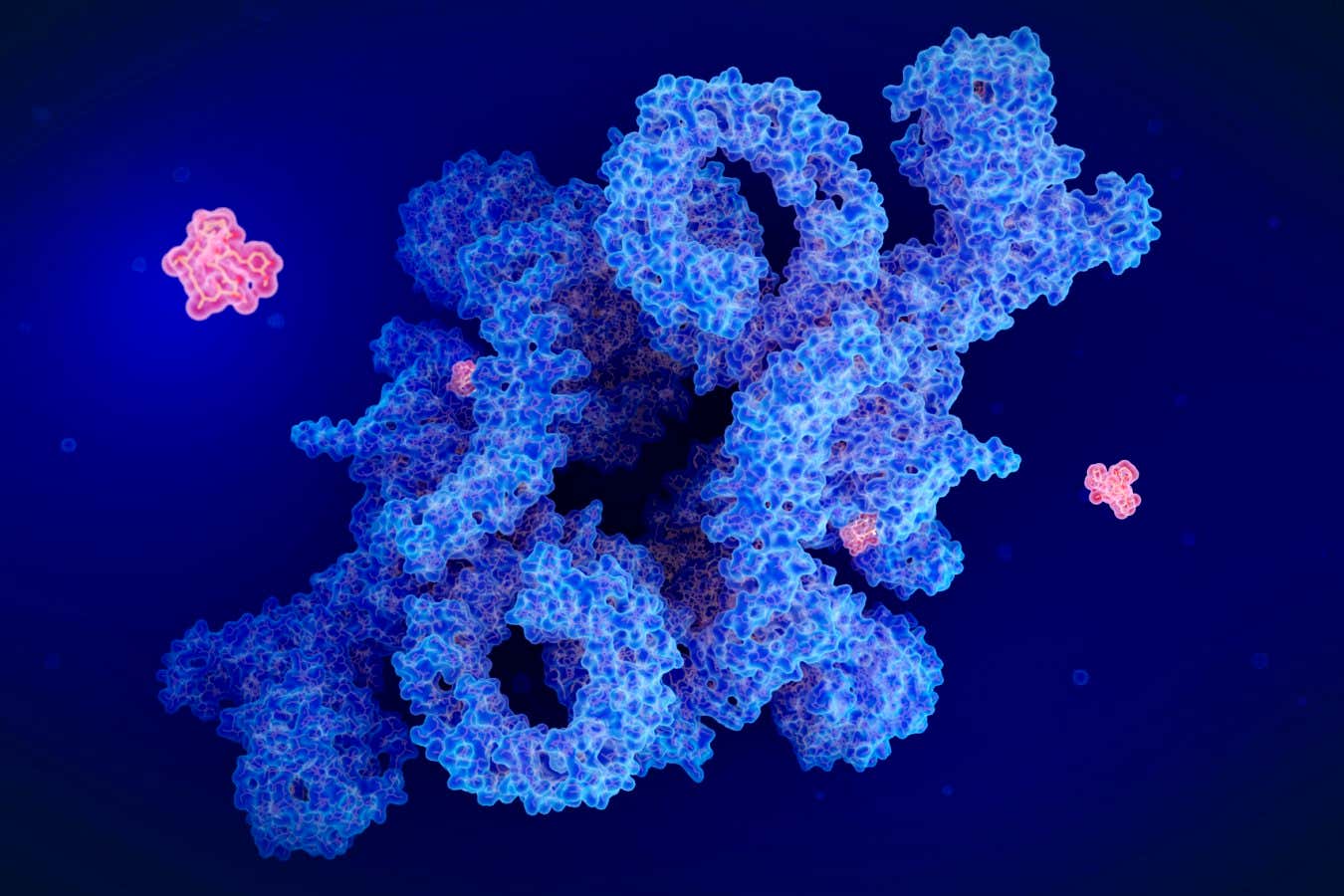
An illustration of the drug rapamycin (red) inhibiting the protein complex mTORC1, which has various effects on cellular function
SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY/Getty Images
The drug rapamycin seems to have more or less the same life-extending effect as restricting calories, according to the largest study yet of longevity in different vertebrate species.
Scientists are investigating whether interventions like dietary tweaks and exercise could help us live longer while reducing the health impacts of ageing. Restricting calorie intake while ensuring essential nutrient needs are met, for example, has been shown to extend the lifespan of non-human animals by as much as 40 per cent.
“Anyone in the field who’s paying attention, I think we all have known for a long time that caloric restriction usually works – and by works, I mean increases lifespan,” says Matt Kaeberlein at the University of Washington in Seattle, who wasn’t involved in the latest research.
Another approach garnering interest is potential anti-ageing drugs, such as rapamycin, which was originally developed as an immunosuppressant. A combination of rapamycin and the cancer drug trametinib was shown earlier this year to increase lifespan in mice by 30 per cent.
Now, Zahida Sultanova at the University of East Anglia, UK, and her colleagues have looked at data from 167 studies of lifespan interventions across eight vertebrate species, including fish, mice, rats and rhesus monkeys, but not humans.
The researchers found that dietary restriction, whether via intermittent fasting or just generally cutting calories, extended the lifespan of all eight species, for both males and females – and rapamycin seems to have roughly the same effect. They also looked into the potential of the type 2 diabetes drug metformin, which has similarly been touted as a potential life-extender, but found no longevity benefit.
People shouldn’t start taking rapamycin off the back of these results, though, says Sultanova. “Rapamycin, especially high doses, has side effects because it is supposed to suppress your immune system,” she says, adding that studies in mice show it can disturb reproduction. Yet preliminary data from one trial recently indicated that low doses of rapamycin are relatively safe in healthy older adults.
Kaeberlein also says that people shouldn’t take any medication or restrict their calorie intake in an attempt to stave off ageing, with the latter being linked to physical weakness and mental health issues. “I think we need to know more about the risk-reward ratio in humans before we can make those sorts of determinations,” he says. “I believe rapamycin will have benefits for some people and we’re learning more and more about who those people are likely to be.”
Other drugs that work similarly to rapamycin, known as rapalogs, could hold more promise if they can extend lifespan with even fewer side effects, says Sultanova.
Kaeberlein says the results fit the patterns he has seen in the literature, but adds that “you always have to be careful when you’re looking across different species because the magnitude of effects that we see in shorter-lived organisms are usually larger than the magnitude we see in longer-lived organisms”.
Topics:
Source link : https://www.newscientist.com/article/2484955-rapamycin-seems-to-boost-longevity-as-effectively-as-eating-less/?utm_campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utm_source=NSNS&utm_medium=RSS&utm_content=home
Author :
Publish date : 2025-06-19 00:01:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.