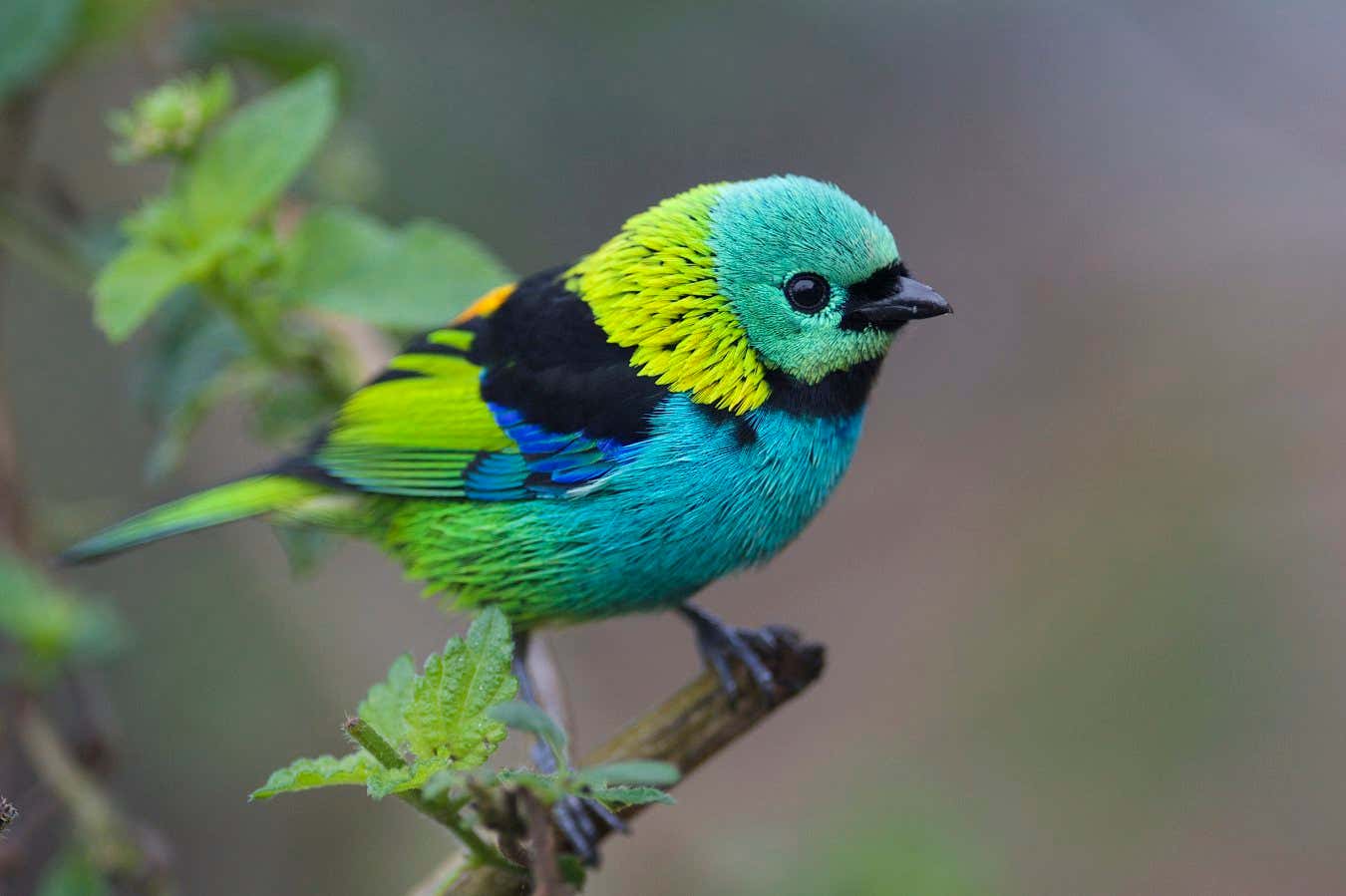
Green-headed tanagers (Tangara seledon) are strikingly colourful
Daniel Field
Brightly coloured songbirds called tanagers are so eye-catching because they have a hidden layer of black or white beneath their dazzling plumage.
Painters often prime a canvas with a layer of white to enhance the colours they will eventually layer on, as well as to make it smoother and stronger. But it seems this is a mechanism that birds were using long before humans picked up paintbrushes.
Rosalyn Price-Waldman at Princeton University and her colleagues have found that when songbirds in the tanager genus Tangara have bright red or yellow plumage, they usually have white layers hidden underneath. When they have blue plumage, they have black layers beneath.
To investigate why, they removed 72 feathers from taxidermied tanager specimens in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County’s collection.
By taking pictures of the feathers on different backgrounds, the team measured how their reflectance or absorption of light changed, finding that the underlayers make the top layers look more colourful.
The red and yellow colouration is created by pigments, which are molecules that selectively absorb light to make colour. This means backscattering light from the white below makes them brighter, says Price-Waldman.
But blue colouration is created by nanostructures within the feathers that selectively scatter light, rather than absorbing light to create the colour we see. Because of this, the light-absorbing black below makes the blue look brighter. “If you have white underneath them, they look a white-grey colour,” says Price-Waldman.
The overall effect of the plumage is created because feathers are layered like tiles on a roof, she says. When you take a single feather, it may have a colourful tip, an intermediate region of either black or white and then the fluffy, downy base. When these feathers are layered on the body, the tips create a contiguous layer of colour, above a contiguous layer of white or black.
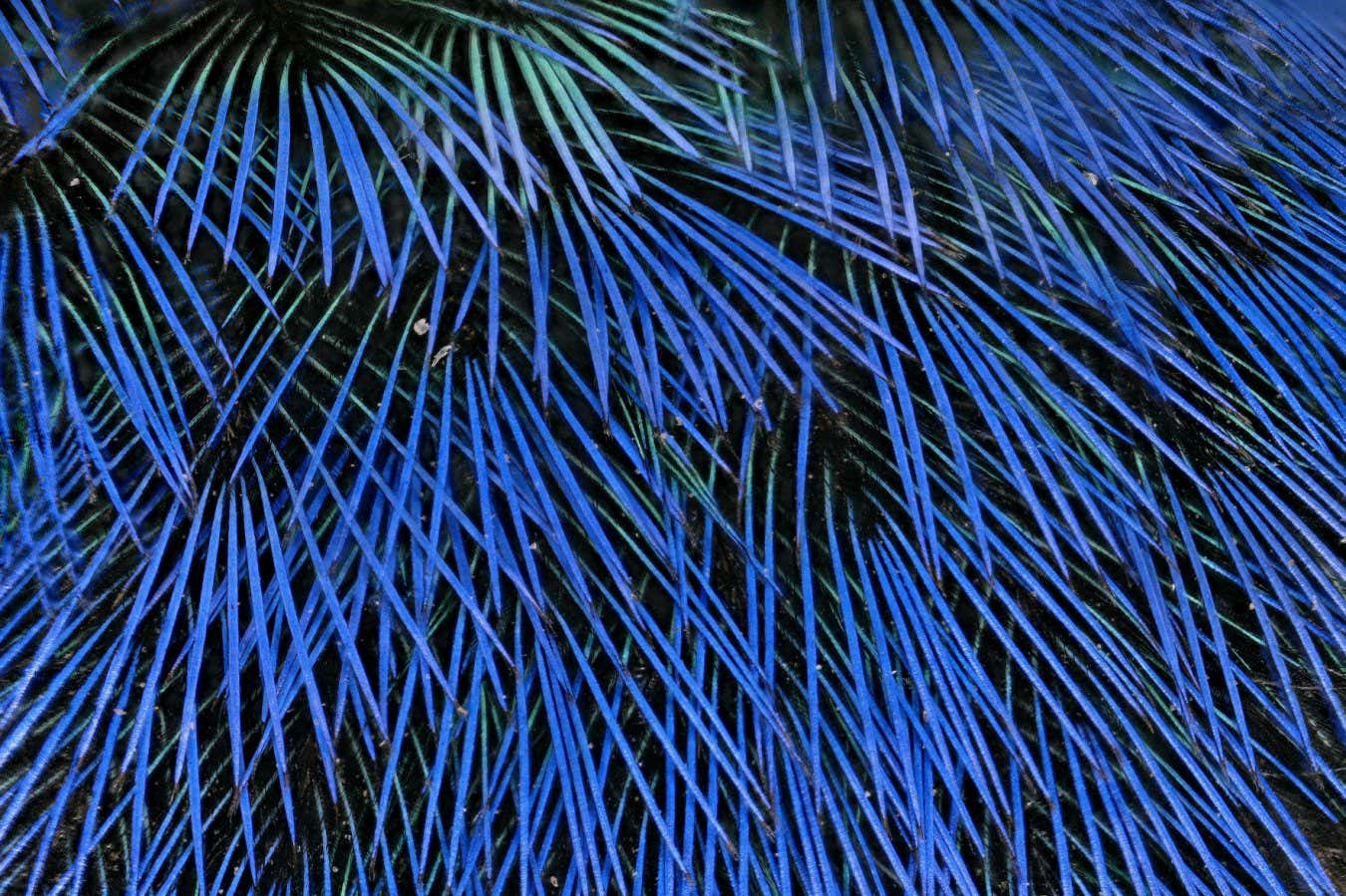

Blue feathers on the crown of a red-necked tanager (Tangara cyanocephala) are intensified by a layer of black plumage underneath
Rosalyn Price-Waldman, Allison Shultz
Price-Waldman and her colleagues also found that, in some cases, these layers of feathers generate the differences in colour between the sexes.
“We found a few cases where the females had black underneath yellow and the males had white underneath yellow,” she says. “When you put their feathers on the same background, the feathers actually look really similar. It’s not until you take the male feathers and put them on white and the female feathers on a black background that you really get the large differences in colouration that you see.”
The researchers found that this colour-boosting strategy is seen in many other songbirds, including manakins and cotingas.
“While a lot of research has already been done to understand how birds produce such striking colours, there is clearly a lot left to discover,” says Chris Cooney at the University of Sheffield, UK. “It appears that this ‘hidden’ mechanism for enhancing the brightness of plumage colours may actually be rather widespread across bird species.”
Topics:
Source link : https://www.newscientist.com/article/2489534-the-secret-to-what-makes-colours-pop-on-dazzling-songbirds/?utm_campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utm_source=NSNS&utm_medium=RSS&utm_content=home
Author :
Publish date : 2025-07-23 19:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.